"We believe one of the most compelling investment opportunities over the next few years is likely to be in companies that serve domestic demand within emerging markets. Our case rests on two underlying and interconnected forces – one economic and the other demographic. As poor countries get richer, they save as much as they can. Savings rates usually rise until countries reach a range of $3,000 to $10,000 per capita GDP. Once in that range, savings rates begin to decline and consumption becomes a larger part of GDP growth as society starts to provide a social safety net. At this level of wealth, per capita consumption of all goods and services rises in a highly non-linear fashion. For example, while Chinese per capita GDP quadrupled from $1,000 to $4,000 during the past decade, auto sales rose from one million vehicles per year to over
17 million. Markets rarely anticipate this kind of non-linear growth. Fifty percent of all emerging markets (by market capitalization) are now in this sweet spot of shifting from savings to
consumption."
Read more in attached newsletter.
1 of 1 File(s)
1 of 1 File(s)
Some very interesting insights into investing, stocks, valuation etc
Excerpts from Berkshire Hathaway Inc Annual Report 2011
To the Shareholders of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The per-share book value of both our Class A and Class B stock increased by 4.6% in 2011. Over the last 47 years (that is, since present management took over), book value has grown from $19 to $99,860, a rate of 19.8% compounded annually.*
Charlie Munger, Berkshire's Vice Chairman and my partner, and I feel good about the company's progress during 2011. Here are the highlights:
• The primary job of a Board of Directors is to see that the right people are running the business and to be sure that the next generation of leaders is identified and ready to take over tomorrow. I have been on 19 corporate boards, and Berkshire's directors are at the top of the list in the time and diligence they have devoted to succession planning. What's more, their efforts have paid off.
• On September 16th we acquired Lubrizol, a worldwide producer of additives and other specialty chemicals. The company has had an outstanding record since James Hambrick became CEO in 2004, with pre-tax profits increasing from $147 million to $1,085 million. Lubrizol will have many opportunities for "bolt-on" acquisitions in the specialty chemical field. Indeed, we've already agreed to three, costing $493 million. James is a disciplined buyer and a superb operator. Charlie and I are eager to expand his managerial domain.
• Our insurance operations continued their delivery of costless capital that funds a myriad of other opportunities. This business produces "float" – money that doesn't belong to us, but that we get to invest for Berkshire's benefit. And if we pay out less in losses and expenses than we receive in premiums, we additionally earn an underwriting profit, meaning the float costs us less than nothing. Though we are sure to have underwriting losses from time to time, we've now had nine consecutive years of underwriting profits, totaling about $17 billion. Over the same nine years our float increased from $41 billion to its current record of $70 billion. Insurance has been good to us.
We view these holdings as partnership interests in wonderful businesses, not as marketable securities to be bought or sold based on their near-term prospects. Our share of their earnings, however, are far from fully reflected in our earnings; only the dividends we receive from these businesses show up in our financial reports. Over time, though, the undistributed earnings of these companies that are attributable to our ownership are of huge importance to us. That's because they will be used in a variety of ways to increase future earnings and dividends of the investee. They may also be devoted to stock repurchases, which will increase our share of the company's future earnings.
Had we owned our present positions throughout last year, our dividends from the "Big Four" would have been $862 million. That's all that would have been reported in Berkshire's income statement. Our share of this quartet's earnings, however, would have been far greater: $3.3 billion. Charlie and I believe that the $2.4 billion that goes unreported on our books creates at least that amount of value for Berkshire as it fuels earnings gains in future years. We expect the combined earnings of the four – and their dividends as well – to increase in 2012 and, for that matter, almost every year for a long time to come. A decade from now, our current holdings of the four companies might well account for earnings of $7 billion, of which $2 billion in dividends would come to us.
• Last year, I told you that "a housing recovery will probably begin within a year or so." I was dead wrong. We have five businesses whose results are significantly influenced by housing activity. The connection is direct at Clayton Homes, which is the largest producer of homes in the country, accounting for about 7% of those constructed during 2011.
Intrinsic Business Value
Charlie and I measure our performance by the rate of gain in Berkshire's per-share intrinsic business value. If our gain over time outstrips the performance of the S&P 500, we have earned our paychecks. If it doesn't, we are overpaid at any price.
We have no way to pinpoint intrinsic value. But we do have a useful, though considerably understated, proxy for it: per-share book value. This yardstick is meaningless at most companies. At Berkshire, however, book value very roughly tracks business values. That's because the amount by which Berkshire's intrinsic value exceeds book value does not swing wildly from year to year, though it increases in most years. Over time, the divergence will likely become ever more substantial in absolute terms, remaining reasonably steady, however, on a percentage basis as both the numerator and denominator of the business-value/book-value equation increase.
Charlie and I like to see gains in both areas, but our primary focus is on building operating earnings. Over time, the businesses we currently own should increase their aggregate earnings, and we hope also to purchase some large operations that will give us a further boost. We now have eight subsidiaries that would each be included in the Fortune 500 were they stand-alone companies. That leaves only 492 to go. My task is clear, and I'm on the prowl.
At our limit price of 110% of book value, repurchases clearly increase Berkshire's per-share intrinsic value. And the more and the cheaper we buy, the greater the gain for continuing shareholders. Therefore, if given the opportunity, we will likely repurchase stock aggressively at our price limit or lower.
Today, IBM has 1.16 billion shares outstanding, of which we own about 63.9 million or 5.5%. Naturally, what happens to the company's earnings over the next five years is of enormous importance to us. Beyond that, the company will likely spend $50 billion or so in those years to repurchase shares. Our quiz for the day: What should a long-term shareholder, such as Berkshire, cheer for during that period?
I won't keep you in suspense. We should wish for IBM's stock price to languish throughout the five years.
Let's do the math. If IBM's stock price averages, say, $200 during the period, the company will acquire 250 million shares for its $50 billion. There would consequently be 910 million shares outstanding, and we would own about 7% of the company. If the stock conversely sells for an average of $300 during the five-year period, IBM will acquire only 167 million shares. That would leave about 990 million shares outstanding after five years, of which we would own 6.5%.
If IBM were to earn, say, $20 billion in the fifth year, our share of those earnings would be a full $100 million greater under the "disappointing" scenario of a lower stock price than they would have been at the higher price. At some later point our shares would be worth perhaps $11⁄2 billion more than if the "high-price" repurchase scenario had taken place.
The logic is simple: If you are going to be a net buyer of stocks in the future, either directly with your own money or indirectly (through your ownership of a company that is repurchasing shares), you are hurt when stocks rise. You benefit when stocks swoon. Emotions, however, too often complicate the matter: Most people, including those who will be net buyers in the future, take comfort in seeing stock prices advance. These shareholders resemble a commuter who rejoices after the price of gas increases, simply because his tank contains a day's supply.
Charlie and I don't expect to win many of you over to our way of thinking – we've observed enough human behavior to know the futility of that – but we do want you to be aware of our personal calculus. And here a confession is in order: In my early days I, too, rejoiced when the market rose. Then I read Chapter Eight of Ben Graham's The Intelligent Investor, the chapter dealing with how investors should view fluctuations in stock prices. Immediately the scales fell from my eyes, and low prices became my friend. Picking up that book was one of the luckiest moments in my life.
First by float size is the Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group, run by Ajit Jain. Ajit insures risks that no one else has the desire or the capital to take on. His operation combines capacity, speed, decisiveness and, most importantly, brains in a manner that is unique in the insurance business. Yet he never exposes Berkshire to risks that are inappropriate in relation to our resources. Indeed, we are far more conservative in that respect than most large insurers. For example, if the insurance industry should experience a $250 billion loss from some mega-catastrophe – a loss about triple anything it has ever faced – Berkshire as a whole would likely record a moderate profit for the year because of its many streams of earnings. Concurrently, all other major insurers and reinsurers would be far in the red, and some would face insolvency.
From a standing start in 1985, Ajit has created an insurance business with float of $34 billion and significant underwriting profits, a feat that no CEO of any other insurer has come close to matching. By these accomplishments, he has added a great many billions of dollars to the value of Berkshire. Charlie would gladly trade me for a second Ajit. Alas, there is none.
Many insurers pass the first three tests and flunk the fourth. They simply can't turn their back on business that their competitors are eagerly writing. That old line, "The other guy is doing it so we must as well," spells trouble in any business, but in none more so than insurance. Indeed, a good underwriter needs an independent mindset akin to that of the senior citizen who received a call from his wife while driving home. "Albert, be careful," she warned, "I just heard on the radio that there's a car going the wrong way down the Interstate." "Mabel, they don't know the half of it," replied Albert, "It's not just one car, there are hundreds of them."
We have two very large businesses, BNSF and MidAmerican Energy, that have important common characteristics distinguishing them from our many other businesses. Consequently, we assign them their own sector in this letter and also split out their combined financial statistics in our GAAP balance sheet and income statement.
A key characteristic of both companies is the huge investment they have in very long-lived, regulated assets, with these partially funded by large amounts of long-term debt that is not guaranteed by Berkshire. Our credit is not needed: Both businesses have earning power that even under terrible business conditions amply covers their interest requirements. In a less than robust economy during 2011, for example, BNSF's interest coverage was 9.5x. At MidAmerican, meanwhile, two key factors ensure its ability to service debt under all circumstances: The stability of earnings that is inherent in our exclusively offering an essential service and a diversity of earnings streams, which shield it from the actions of any single regulatory body.
Measured by ton-miles, rail moves 42% of America's inter-city freight, and BNSF moves more than any other railroad – about 37% of the industry total. A little math will tell you that about 15% of all inter-city ton-miles of freight in the U.S. is transported by BNSF. It is no exaggeration to characterize railroads as the circulatory system of our economy. Your railroad is the largest artery.
Massive investments of the sort that BNSF is making would be foolish if it could not earn appropriate returns on the incremental sums it commits. But I am confident it will do so because of the value it delivers. Many years ago Ben Franklin counseled, "Keep thy shop, and thy shop will keep thee." Translating this to our regulated businesses, he might today say, "Take care of your customer, and the regulator – your customer's representative – will take care of you." Good behavior by each party begets good behavior in return.
This group of companies sells products ranging from lollipops to jet airplanes. Some of the businesses enjoy terrific economics, measured by earnings on unleveraged net tangible assets that run from 25% after-tax to more than 100%. Others produce good returns in the area of 12-20%. A few, however, have very poor returns, a result of some serious mistakes I made in my job of capital allocation. These errors came about because I misjudged either the competitive strength of the business being purchased or the future economics of the industry in which it operated. I try to look out ten or twenty years when making an acquisition, but sometimes my eyesight has been poor. Charlie's has been better; he voted no more than "present" on several of my errant purchases.
Please understand, however, that Charlie and I are neither masochists nor Pollyannas. If either of the failings we set forth in Rule 11 is present – if the business will likely be a cash drain over the longer term, or if labor strife is endemic – we will take prompt and decisive action. Such a situation has happened only a couple of times in our 47-year history, and none of the businesses we now own is in straits requiring us to consider disposing of it.
The profile of the remaining 2011 earnings – $4,387 million – illustrates the comeback of much of America from the devastation wrought by the 2008 financial panic. Though housing-related businesses remain in the emergency room, most other businesses have left the hospital with their health fully restored.
It's a joy to watch Marmon's progress under Frank Ptak's leadership. In addition to achieving internal growth, Frank regularly makes bolt-on acquisitions that, in aggregate, will materially increase Marmon's earning power. (He did three, costing about $270 million, in the last few months.) Joint ventures around the world are another opportunity for Marmon. At midyear Marmon partnered with the Kundalia family in an Indian crane operation that is already delivering substantial profits. This is Marmon's second venture with the family, following a successful wire and cable partnership instituted a few years ago.
Of the eleven major sectors in which Marmon operates, ten delivered gains in earnings last year. You can be confident of higher earnings from Marmon in the years ahead.
• "Buy commodities, sell brands" has long been a formula for business success. It has produced enormous and sustained profits for Coca-Cola since 1886 and Wrigley since 1891. On a smaller scale, we have enjoyed good fortune with this approach at See's Candy since we purchased it 40 years ago.
Last year See's had record pre-tax earnings of $83 million, bringing its total since we bought it to $1.65 billion. Contrast that figure with our purchase price of $25 million and our yearend carrying-value (net of cash) of less than zero. (Yes, you read that right; capital employed at See's fluctuates seasonally, hitting a low after Christmas.) Credit Brad Kinstler for taking the company to new heights since he became CEO in 2006.
Our experience with NFM and the Blumkin family that runs it has been a real joy. The business was built by Rose Blumkin (known to all as "Mrs. B"), who started the company in 1937 with $500 and a dream. She sold me our interest when she was 89 and worked until she was 103. (After retiring, she died the next year, a sequence I point out to any other Berkshire manager who even thinks of retiring.)
Overall, the intrinsic value of the businesses in this Berkshire sector significantly exceeds their book value. For many of the smaller companies, however, this is not true. I have made more than my share of mistakes buying small companies. Charlie long ago told me, "If something's not worth doing at all, it's not worth doing well," and I should have listened harder. In any event, our large purchases have generally worked well – extraordinarily well in a few cases – and overall this sector is a winner for us.
Certain shareholders have told me they hunger for more discussions of accounting arcana. So here's a bit of GAAP-mandated nonsense I hope both of them enjoy.
Common sense would tell you that our varied subsidiaries should be carried on our books at their cost plus the earnings they have retained since our purchase (unless their economic value has materially decreased, in which case an appropriate write-down must be taken). And that's essentially the reality at Berkshire – except for the weird situation at Marmon.
As is well-known, the U.S. went off the rails in its home-ownership and mortgage-lending policies, and for these mistakes our economy is now paying a huge price. All of us participated in the destructive behavior – government, lenders, borrowers, the media, rating agencies, you name it. At the core of the folly was the almost universal belief that the value of houses was certain to increase over time and that any dips would be inconsequential. The acceptance of this premise justified almost any price and practice in housing transactions. Homeowners everywhere felt richer and rushed to "monetize" the increased value of their homes by refinancings. These massive cash infusions fueled a consumption binge throughout our economy. It all seemed great fun while it lasted. (A largely unnoted fact: Large numbers of people who have "lost" their house through foreclosure have actually realized a profit because they carried out refinancings earlier that gave them cash in excess of their cost. In these cases, the evicted homeowner was the winner, and the victim was the lender.)
In 2007, the bubble burst, just as all bubbles must. We are now in the fourth year of a cure that, though long and painful, is sure to succeed. Today, household formations are consistently exceeding housing starts.
As was the case with Coca-Cola in 1988 and the railroads in 2006, I was late to the IBM party. I have been reading the company's annual report for more than 50 years, but it wasn't until a Saturday in March last year that my thinking crystallized. As Thoreau said, "It's not what you look at that matters, it's what you see."
One additional point about these two new arrivals. Both Ted and Todd will be helpful to the next CEO of Berkshire in making acquisitions. They have excellent "business minds" that grasp the economic forces likely to determine the future of a wide variety of businesses. They are aided in their thinking by an understanding of what is predictable and what is unknowable.
Charlie and I continue to believe that our equity-put positions will produce a significant profit, considering both the $4.2 billion of float we will have held for more than fifteen years and the $222 million profit we've already realized on contracts that we repurchased. At yearend, Berkshire's book value reflected a liability of $8.5 billion for the remaining contracts; if they had all come due at that time our payment would have been $6.2 billion.
The Basic Choices for Investors and the One We Strongly Prefer
Investing is often described as the process of laying out money now in the expectation of receiving more money in the future. At Berkshire we take a more demanding approach, defining investing as the transfer to others of purchasing power now with the reasoned expectation of receiving more purchasing power – after taxes have been paid on nominal gains – in the future. More succinctly, investing is forgoing consumption now in order to have the ability to consume more at a later date.
From our definition there flows an important corollary: The riskiness of an investment is not measured by beta (a Wall Street term encompassing volatility and often used in measuring risk) but rather by the probability – the reasoned probability – of that investment causing its owner a loss of purchasing-power over his contemplated holding period. Assets can fluctuate greatly in price and not be risky as long as they are reasonably certain to deliver increased purchasing power over their holding period. And as we will see, a non-fluctuating asset can be laden with risk.
Investment possibilities are both many and varied. There are three major categories, however, and it's important to understand the characteristics of each. So let's survey the field.
• Investments that are denominated in a given currency include money-market funds, bonds, mortgages, bank deposits, and other instruments. Most of these currency-based investments are thought of as "safe." In truth they are among the most dangerous of assets. Their beta may be zero, but their risk is huge. Over the past century these instruments have destroyed the purchasing power of investors in many countries, even as the holders continued to receive timely payments of interest and principal. This ugly result, moreover, will forever recur. Governments determine the ultimate value of money, and systemic forces will sometimes cause them to gravitate to policies that produce inflation. From time to time such policies spin out of control.
Even in the U.S., where the wish for a stable currency is strong, the dollar has fallen a staggering 86% in value since 1965, when I took over management of Berkshire. It takes no less than $7 today to buy what $1 did at that time. Consequently, a tax-free institution would have needed 4.3% interest annually from bond investments over that period to simply maintain its purchasing power. Its managers would have been kidding themselves if they thought of any portion of that interest as "income."
For tax-paying investors like you and me, the picture has been far worse. During the same 47-year period, continuous rolling of U.S. Treasury bills produced 5.7% annually. That sounds satisfactory. But if an individual investor paid personal income taxes at a rate averaging 25%, this 5.7% return would have yielded nothing in the way of real income. This investor's visible income tax would have stripped him of 1.4 points of the stated yield, and the invisible inflation tax would have devoured the remaining 4.3 points. It's noteworthy that the implicit inflation "tax" was more than triple the explicit income tax that our investor probably thought of as his main burden. "In God We Trust" may be imprinted on our currency, but the hand that activates our government's printing press has been all too human.
High interest rates, of course, can compensate purchasers for the inflation risk they face with currency-based investments – and indeed, rates in the early 1980s did that job nicely. Current rates, however, do not come close to offsetting the purchasing-power risk that investors assume. Right now bonds should come with a warning label.
Under today's conditions, therefore, I do not like currency-based investments. Even so, Berkshire holds significant amounts of them, primarily of the short-term variety. At Berkshire the need for ample liquidity occupies center stage and will never be slighted, however inadequate rates may be. Accommodating this need, we primarily hold U.S. Treasury bills, the only investment that can be counted on for liquidity under the most chaotic of economic conditions. Our working level for liquidity is $20 billion; $10 billion is our absolute minimum.
Beyond the requirements that liquidity and regulators impose on us, we will purchase currency-related securities only if they offer the possibility of unusual gain – either because a particular credit is mispriced, as can occur in periodic junk-bond debacles, or because rates rise to a level that offers the possibility of realizing substantial capital gains on high-grade bonds when rates fall. Though we've exploited both opportunities in the past – and may do so again – we are now 180 degrees removed from such prospects. Today, a wry comment that Wall Streeter Shelby Cullom Davis made long ago seems apt: "Bonds promoted as offering risk-free returns are now priced to deliver return-free risk."
• The second major category of investments involves assets that will never produce anything, but that are purchased in the buyer's hope that someone else – who also knows that the assets will be forever unproductive – will pay more for them in the future. Tulips, of all things, briefly became a favorite of such buyers in the 17th century.
This type of investment requires an expanding pool of buyers, who, in turn, are enticed because they believe the buying pool will expand still further. Owners are not inspired by what the asset itself can produce – it will remain lifeless forever – but rather by the belief that others will desire it even more avidly in the future.
The major asset in this category is gold, currently a huge favorite of investors who fear almost all other assets, especially paper money (of whose value, as noted, they are right to be fearful). Gold, however, has two significant shortcomings, being neither of much use nor procreative. True, gold has some industrial and decorative utility, but the demand for these purposes is both limited and incapable of soaking up new production. Meanwhile, if you own one ounce of gold for an eternity, you will still own one ounce at its end.
What motivates most gold purchasers is their belief that the ranks of the fearful will grow. During the past decade that belief has proved correct. Beyond that, the rising price has on its own generated additional buying enthusiasm, attracting purchasers who see the rise as validating an investment thesis. As "bandwagon" investors join any party, they create their own truth – for a while.
Over the past 15 years, both Internet stocks and houses have demonstrated the extraordinary excesses that can be created by combining an initially sensible thesis with well-publicized rising prices. In these bubbles, an army of originally skeptical investors succumbed to the "proof" delivered by the market, and the pool of buyers – for a time – expanded sufficiently to keep the bandwagon rolling. But bubbles blown large enough inevitably pop. And then the old proverb is confirmed once again: "What the wise man does in the beginning, the fool does in the end."
Today the world's gold stock is about 170,000 metric tons. If all of this gold were melded together, it would form a cube of about 68 feet per side. (Picture it fitting comfortably within a baseball infield.) At $1,750 per ounce – gold's price as I write this – its value would be $9.6 trillion. Call this cube pile A.
Let's now create a pile B costing an equal amount. For that, we could buy all U.S. cropland (400 million acres with output of about $200 billion annually), plus 16 Exxon Mobils (the world's most profitable company, one earning more than $40 billion annually). After these purchases, we would have about $1 trillion left over for walking-around money (no sense feeling strapped after this buying binge). Can you imagine an investor with $9.6 trillion selecting pile A over pile B?
Beyond the staggering valuation given the existing stock of gold, current prices make today's annual production of gold command about $160 billion. Buyers – whether jewelry and industrial users, frightened individuals, or speculators – must continually absorb this additional supply to merely maintain an equilibrium at present prices.
A century from now the 400 million acres of farmland will have produced staggering amounts of corn, wheat, cotton, and other crops – and will continue to produce that valuable bounty, whatever the currency may be. Exxon Mobil will probably have delivered trillions of dollars in dividends to its owners and will also hold assets worth many more trillions (and, remember, you get 16 Exxons). The 170,000 tons of gold will be unchanged in size and still incapable of producing anything. You can fondle the cube, but it will not respond.
Admittedly, when people a century from now are fearful, it's likely many will still rush to gold. I'm confident, however, that the $9.6 trillion current valuation of pile A will compound over the century at a rate far inferior to that achieved by pile B.
• Our first two categories enjoy maximum popularity at peaks of fear: Terror over economic collapse drives individuals to currency-based assets, most particularly U.S. obligations, and fear of currency collapse fosters movement to sterile assets such as gold. We heard "cash is king" in late 2008, just when cash should have been deployed rather than held. Similarly, we heard "cash is trash" in the early 1980s just when fixed-dollar investments were at their most attractive level in memory. On those occasions, investors who required a supportive crowd paid dearly for that comfort.
My own preference – and you knew this was coming – is our third category: investment in productive assets, whether businesses, farms, or real estate. Ideally, these assets should have the ability in inflationary times to deliver output that will retain its purchasing-power value while requiring a minimum of new capital investment. Farms, real estate, and many businesses such as Coca-Cola, IBM and our own See's Candy meet that double-barreled test. Certain other companies – think of our regulated utilities, for example – fail it because inflation places heavy capital requirements on them. To earn more, their owners must invest more. Even so, these investments will remain superior to nonproductive or currency-based assets.
Whether the currency a century from now is based on gold, seashells, shark teeth, or a piece of paper (as today), people will be willing to exchange a couple of minutes of their daily labor for a Coca-Cola or some See's peanut brittle. In the future the U.S. population will move more goods, consume more food, and require more living space than it does now. People will forever exchange what they produce for what others produce.
Our country's businesses will continue to efficiently deliver goods and services wanted by our citizens. Metaphorically, these commercial "cows" will live for centuries and give ever greater quantities of "milk" to boot. Their value will be determined not by the medium of exchange but rather by their capacity to deliver milk. Proceeds from the sale of the milk will compound for the owners of the cows, just as they did during the 20th century when the Dow increased from 66 to 11,497 (and paid loads of dividends as well). Berkshire's goal will be to increase its ownership of first-class businesses. Our first choice will be to own them in their entirety – but we will also be owners by way of holding sizable amounts of marketable stocks. I believe that over any extended period of time this category of investing will prove to be the runaway winner among the three we've examined. More important, it will be by far the safest.
The Annual Meeting
The annual meeting will be held on Saturday, May 5th at the CenturyLink Center (renamed from "Qwest"). Last year, Carrie Kizer debuted as the ringmaster and earned a lifetime assignment. Everyone loved the job she did – especially me.
BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC. ACQUISITION CRITERIA
We are eager to hear from principals or their representatives about businesses that meet all of the following criteria:
(1) Large purchases (at least $75 million of pre-tax earnings unless the business will fit into one of our existing units),
(2) Demonstrated consistent earning power (future projections are of no interest to us, nor are "turnaround" situations),
(3) Businesses earning good returns on equity while employing little or no debt,
(4) Management in place (we can't supply it),
(5) Simple businesses (if there's lots of technology, we won't understand it),
(6) An offering price (we don't want to waste our time or that of the seller by talking, even preliminarily, about a transaction when price is unknown).
The larger the company, the greater will be our interest: We would like to make an acquisition in the $5-20 billion range. We are not interested, however, in receiving suggestions about purchases we might make in the general stock market. We will not engage in unfriendly takeovers. We can promise complete confidentiality and a very fast answer – customarily within five minutes – as to whether we're interested. We prefer to buy for cash, but will consider issuing stock when we receive as much in intrinsic business value as we give. We don't participate in auctions.
Charlie and I frequently get approached about acquisitions that don't come close to meeting our tests: We've found that if you advertise an interest in buying collies, a lot of people will call hoping to sell you their cocker spaniels. A line from a country song expresses our feeling about new ventures, turnarounds, or auction-like sales: "When the phone don't ring, you'll know it's me."
MANAGEMENT'S
BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC.
INTRINSIC VALUE – TODAY AND TOMORROW *
Though Berkshire's intrinsic value cannot be precisely calculated, two of its three key pillars can be measured. Charlie and I rely heavily on these measurements when we make our own estimates of Berkshire's value. The first component of value is our investments: stocks, bonds and cash equivalents. At yearend these totaled $158 billion at market value.
Insurance float – money we temporarily hold in our insurance operations that does not belong to us – funds $66 billion of our investments. This float is "free" as long as insurance underwriting breaks even, meaning that the premiums we receive equal the losses and expenses we incur. Of course, underwriting results are volatile, swinging erratically between profits and losses. Over our entire history, though, we've been significantly profitable, and I also expect us to average breakeven results or better in the future. If we do that, all of our investments – those funded both by float and by retained earnings – can be viewed as an element of value for Berkshire shareholders.
Berkshire's second component of value is earnings that come from sources other than investments and insurance underwriting. These earnings are delivered by our 68 non-insurance companies, itemized on page 106. In Berkshire's early years, we focused on the investment side. During the past two decades, however, we've increasingly emphasized the development of earnings from non-insurance businesses, a practice that will continue.
The following tables illustrate this shift. In the first table, we present per-share investments at decade intervals beginning in 1970, three years after we entered the insurance business. We exclude those investments applicable to minority interests.
Though our compounded annual increase in per-share investments was a healthy 19.9% over the 40-year period, our rate of increase has slowed sharply as we have focused on using funds to buy operating businesses. The payoff from this shift is shown in the following table, which illustrates how earnings of our non-insurance businesses have increased, again on a per-share basis and after applicable minority interests.
Year Per-Share Pre-Tax Earnings Period Compounded Annual Increase in Per-Share Pre-Tax Earnings
For the forty years, our compounded annual gain in pre-tax, non-insurance earnings per share is 21.0%. During the same period, Berkshire's stock price increased at a rate of 22.1% annually. Over time, you can expect our stock price to move in rough tandem with Berkshire's investments and earnings. Market price and intrinsic value often follow very different paths – sometimes for extended periods – but eventually they meet.
There is a third, more subjective, element to an intrinsic value calculation that can be either positive or negative: the efficacy with which retained earnings will be deployed in the future. We, as well as many other businesses, are likely to retain earnings over the next decade that will equal, or even exceed, the capital we presently employ. Some companies will turn these retained dollars into fifty-cent pieces, others into two-dollar bills.
* Reproduced from Berkshire Hathaway Inc. 2010 Annual Report.
This "what-will-they-do-with-the-money" factor must always be evaluated along with the "what-do-we-have-now" calculation in order for us, or anybody, to arrive at a sensible estimate of a company's intrinsic value. That's because an outside investor stands by helplessly as management reinvests his share of the company's earnings. If a CEO can be expected to do this job well, the reinvestment prospects add to the company's current value; if the CEO's talents or motives are suspect, today's value must be discounted. The difference in outcome can be huge. A dollar of then-value in the hands of Sears Roebuck's or Montgomery Ward's CEOs in the late 1960s had a far different destiny than did a dollar entrusted to Sam Walton.
Copyright© 2012 By Warren E. Buffett, All Rights Reserved
Source: http://www.berkshirehathaway.com/2011ar/linksannual11.html
Unintended Consequences
By: Eric Sprott & David Baker 2012 is proving to be the 'Year of the Central Bank'.
It is an exciting celebration of all the wonderful maneuvers central banks can employ to keep the system from falling apart.
Western central banks have gone into complete overdrive since last November, convening, colluding and printing their way out of the mess that is the Eurozone.
The scale and frequency of their maneuvering seems to increase with every passing week, and speaks to the desperate fragility that continues to define much of the financial system today.
The first major maneuver took place on November 30, 2011, when the world's G6 central banks (the Federal Reserve, the Bank of England, the Bank of Japan, the European Central Bank [ECB], the Swiss National Bank, and the Bank of Canada) announced "coordinated actions to enhance their capacity to provide liquidity support to the global financial system".
Long story short, in an effort to avert a total collapse in the European banking system, the US Fed agreed to offer unlimited US dollar swap agreements with the other central banks. These US dollar
swaps allow the other central banks, most notably the ECB, to borrow US dollars from the Federal Reserve and lend them to their respective national banks to meet withdrawals and make debt payments. The best part about these swaps is that they are limitless in scope – meaning that until February 1, 2013, the Federal Reserve is, and will be, prepared to lend as many US dollars as it takes to keep the financial system from imploding. It sounds absolutely great, and the Europeans should be nothing but thankful, except for the tiny little fact that to supply these unlimited US dollars, the Federal Reserve will have to print them out of thin air.
Don't worry, it gets better. Since unlimited US swap lines weren't enough to solve the problem, roughly three weeks later, on December 21, 2011, the European Central Bank launched the first tranche of its lauded Long Term Refinancing Operation (LTRO). This is the program where the ECB flooded 523 separate European banks with 489 billion euros worth of 3-year loans to keep them going through Christmas. A second tranche of LTRO loans is planned to launch at the end of February, with expectations for size ranging from 300 billion to more than 1 trillion euros of uptake.
The good news is that Italian, Portuguese and Spanish bond yields have dropped since the first LTRO went through, which suggests that at least some of the initial LTRO funds have been reinvested back into sovereign debt auctions. The bad news is that the Eurozone banks may now be hooked on what is clearly a back-door quantitative easing (QE) program, and as the warning goes for addictive drugs – once you start, it can be very hard to stop.
Britain is definitely hooked. On February 9, 2012, the Bank of England announced another QE extension for 50 billion pounds, raising their total QE print to £325 billion since March 2009.
Japan's hooked as well. On February 14, 2012, the Bank of Japan announced a ¥10 trillion ($129 billion) expansion to its own QE program, raising its total QE program to ¥65 trillion ($825 billion).
Not to be outdone, in the most recent Fed news conference, US Fed Chairman Bernanke signaled that the Fed will keep interest rates near zero until late 2014, which is 18 months later than he
had promised in Fed meetings last year. If Bernanke keeps his word, by the end of 2014 the US government will have enjoyed near zero interest rates for six years in a row. Granted, extended zero percent interest rates is not nearly as satisfying as a proper QE program, but who needs traditional QE when the Fed already buys 91 percent of all 20-30 year maturity US Treasury bonds?
Perhaps they're saving traditional QE for the upcoming election.
Not to be outdone, in the most recent Fed news conference, US Fed Chairman Bernanke signaled that the Fed will keep interest rates near zero until late 2014, which is 18 months later than he
had promised in Fed meetings last year. If Bernanke keeps his word, by the end of 2014 the US government will have enjoyed near zero interest rates for six years in a row. Granted, extended zero percent interest rates is not nearly as satisfying as a proper QE program, but who needs traditional QE when the Fed already buys 91 percent of all 20-30 year maturity US Treasury bonds?
Perhaps they're saving traditional QE for the upcoming election.
All of this pervasive intervention most likely explains more than 90 percent of the market's positive performance this past January. Had the G6 NOT convened on swaps, had the ECB NOT launched the LTRO programs, and had Bernanke NOT expressed a continuation of zero interest rates, one wonders where the equity indices would trade today. One also wonders if the European banking system would have made it through December. Thank goodness for "coordinated action". It does work in the short-term.
But what about the long-term? What are the unintended consequences of repeatedly juicing the system? What are the repercussions of all this money printing? We can think of a few.
First and foremost, without continued central bank support, interbank liquidity may cease to function entirely in the coming year. Consider the implications of the ECB's LTRO program: when you create a loan program to save the EU banks and make its participation voluntary, every one of those 523 banks that participates is essentially admitting that they have a problem. How will they ever lend money to each other again? If you're a bank that participated in the LTRO program because you were on the verge of bankruptcy, how can you possibly trust other banks that took advantage of the same program?
The ECB's LTRO program has the potential to be very dangerous, because if the EU banks start to rely on the loans too heavily, the ECB may find itself inadvertently attached to the broken EU banking system forever.
The second unintended consequence is the impact that interventions have had on the non-G6 countries' perception of western solvency. If you're a foreign lender to the United States, Britain, Europe or Japan today, how comfortable can you possibly be in lending them money? How do you lend to countries whose sole basis as a going concern rests in their ability to wrangle cash injections printed by their respective central banks? Going further, what happens when the rest of the world, the non-G6 world, starts to question the G6 Central Banks themselves? What entity exists to bailout the financial system if the market moves against the Fed or the ECB?
The fact remains that there are few rungs left in the financial confidence chain in 2012, and central banks may end up pushing their printing schemes too far. In 2008-2009, it was the banks that lost credibility and required massive bailouts by their respective sovereign states. In 2010-2011, it was the sovereigns, most notably those in Europe, that lost credibility and required massive bailouts by their respective central banks. But there is no lender of last resort for the central banks themselves. That the IMF is now trying to raise another $600 billion as a security buffer doesn't go unnoticed, but do they honestly think that's going to make any difference?
When reviewing today's macro environment, we keep coming back to the same conclusion. The non-G6 world isn't blind to the efforts of the Fed and the ECB. When the Fed openly targets a 2 percent inflation rate, foreign lenders know that means they will lose, at a minimum, at least 2 percent of purchasing power on their US loans in 2012. It therefore shouldn't surprise anyone to see those lenders piling into alternative assets that have a better chance at protecting their wealth, long-term.
This is likely why China reduced its US Treasury exposure by $32 billion in the month of December
This is also why China, which produced 360 tonnes of gold internally last year, also imported an additional 428 tonnes in 2011, up from 119 tonnes in 2010.This may also be why China's copper imports hit a record high of 508,942 tonnes in December 2011, up 47.7 percent from the previous year, despite the fact that their GDP declined at year-end.
Same goes for their crude oil imports, which hit a record high of 23.41 million metric tons this past January, up 7.4 percent year-over-year.
The second unintended consequence is the impact that interventions have had on the non-G6 countries' perception of western solvency. If you're a foreign lender to the United States, Britain, Europe or Japan today, how comfortable can you possibly be in lending them money? How do you lend to countries whose sole basis as a going concern rests in their ability to wrangle cash injections printed by their respective central banks? Going further, what happens when the rest of the world, the non-G6 world, starts to question the G6 Central Banks themselves? What entity exists to bailout the financial system if the market moves against the Fed or the ECB?
The fact remains that there are few rungs left in the financial confidence chain in 2012, and central banks may end up pushing their printing schemes too far. In 2008-2009, it was the banks that lost credibility and required massive bailouts by their respective sovereign states. In 2010-2011, it was the sovereigns, most notably those in Europe, that lost credibility and required massive bailouts by their respective central banks. But there is no lender of last resort for the central banks themselves. That the IMF is now trying to raise another $600 billion as a security buffer doesn't go unnoticed, but do they honestly think that's going to make any difference?
When reviewing today's macro environment, we keep coming back to the same conclusion. The non-G6 world isn't blind to the efforts of the Fed and the ECB. When the Fed openly targets a 2 percent inflation rate, foreign lenders know that means they will lose, at a minimum, at least 2 percent of purchasing power on their US loans in 2012. It therefore shouldn't surprise anyone to see those lenders piling into alternative assets that have a better chance at protecting their wealth, long-term.
This is likely why China reduced its US Treasury exposure by $32 billion in the month of December
This is also why China, which produced 360 tonnes of gold internally last year, also imported an additional 428 tonnes in 2011, up from 119 tonnes in 2010.This may also be why China's copper imports hit a record high of 508,942 tonnes in December 2011, up 47.7 percent from the previous year, despite the fact that their GDP declined at year-end.
Same goes for their crude oil imports, which hit a record high of 23.41 million metric tons this past January, up 7.4 percent year-over-year.
The so-called experts have a habit of downplaying these numbers, but it seems pretty clear to us: China isn't waiting around for next QE program. They are accelerating their move away from paper currencies and into hard assets.
China is not alone in this trend either. Russia has reportedly cut its US Treasury exposure by half since October 2010 (See Figure 2). Not surprisingly, Russia was also a big buyer of gold in 2011, adding approximately 95 tonnes to its gold reserves, with 33 tonnes added in the fourth quarter alone.
It's not hard to envision higher gold prices if the rest of the non-G6 countries follow-suit.
The problem with central bank intervention is that it never works out as planned. The unintended consequences end up cancelling out the short-term benefits. Back in 2008, when the Fed introduced zero percent interest rates, everyone thought it was a great policy. Four years later, however, and we're finally beginning to appreciate the complete destruction it has wreaked on savers. Just look at the horror show that is the pension industry today:
China is not alone in this trend either. Russia has reportedly cut its US Treasury exposure by half since October 2010 (See Figure 2). Not surprisingly, Russia was also a big buyer of gold in 2011, adding approximately 95 tonnes to its gold reserves, with 33 tonnes added in the fourth quarter alone.
It's not hard to envision higher gold prices if the rest of the non-G6 countries follow-suit.
The problem with central bank intervention is that it never works out as planned. The unintended consequences end up cancelling out the short-term benefits. Back in 2008, when the Fed introduced zero percent interest rates, everyone thought it was a great policy. Four years later, however, and we're finally beginning to appreciate the complete destruction it has wreaked on savers. Just look at the horror show that is the pension industry today:
According to Credit Suisse, of the 341 companies in the S&P 500 index with defined benefit pension plans, 97 percent are underfunded today.
According to a recent pension study by Seattle-based Milliman Inc., the combined deficit of the 100 largest defined-benefit plans in the US increased by $236.4 billion in 2011 alone.
According to a recent pension study by Seattle-based Milliman Inc., the combined deficit of the 100 largest defined-benefit plans in the US increased by $236.4 billion in 2011 alone.
The main culprit for the increase? Depressed interest rates on government bonds.
Let's also not forget the public sector pension shortfalls, which are outright frightening. In Europe, unfunded state pension obligations are estimated to total $39 trillion dollars, which is approximately five times higher than Europe's combined gross debt.
In the United States, unfunded pension obligations increased by $2.9 trillion in 2011. If the US
actually acknowledged these costs in their deficit calculations, their official 2011 fiscal deficit would have risen from the reported $1.3 trillion to $4.2 trillion.
Written the long way, that's a deficit of $4,200,000,000,000,… in one year.
There is unfortunately no economic textbook to guide us through these strange times, but common sense suggests we should be extremely wary of the continued maneuvering by central banks. The more central banks print to save the system, the more the system will rely on their printing to stay solvent – and you cannot solve a debt problem with more debt, and you cannot print money without serious repercussions. The central banks are fueling a growing distrust among the creditor nations that is forcing them to take pre-emptive actions with their currency reserves.
Individual investors should take note and follow-suit, because it will be a lot easier to enjoy the
"Year of the Central Bank" if you own things that can actually benefit from all their printing, as opposed to things that can only be destroyed by it.
State-owned IDBI Bank on Friday said it proposes to sell 5 per cent stake to Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) on preferential basis.
LIC has in-principle given approval for subscribing maximum up to 5 per cent of the pre-issue paid up equity capital of the bank, IDBI Bank said in filing on the BSE.
LIC has in-principle given approval for subscribing maximum up to 5 per cent of the pre-issue paid up equity capital of the bank, IDBI Bank said in filing on the BSE.
Hedge funds and professional investors are always looking for countries with lower interest rates where borrowing is cheaper and then invest the same in countries with higher interest rates. Earlier, it was the Japanese yen that gave them this opportunity. After the Lehman crash, the dollar became the funding currency of choice. Investors sold dollars where interest rates were low and purchased currencies like the Indian rupee where the interest rates were high. This carry trade is now moving to the euro.
According to a recent Morgan Stanley report, euro rates are now on a declining trend. Morgan Stanley expects euro rates to fall below the average G10 carry in 2010. They feel that the euro will become a funding currency of choice in 2012 as US rates are moving higher on a relative basis reducing the dollar's attraction for investors. The present US fed rate is at 0.12 percent which has gone up from 0.07 percent over the last three months. The European benchmark key interst rate is at 1 percent which has fallen from 1.25 percent over the same period.
 | |
"The euro yields are below the G10 currencies, just like the US dollar yields were five years ago. We expect the euro to be a depreciating currency.
The US dollar is becoming the carry currency with improving yields and appreciation. So, the Sensex correlations with the euro will rise. The difference it makes to the equity markets is that every time the euro depreciates, it may trigger a rise in Indian equities and vice versa," says Ridham Desai, managing director-research, Morgan Stanley.
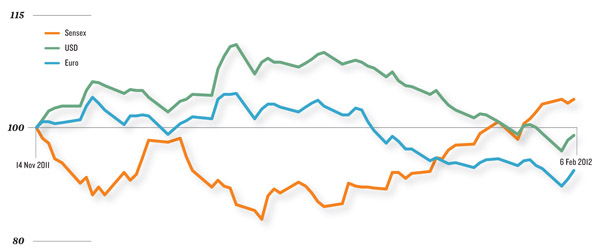
"Investors will borrow in euro and then convert the same into rupee. The next leg would be to sell the euro and then buy the rupee which would depreciate the euro and appreciate the rupee. The market should move higher on account of higher flows," says Manis Thanawala of Greenback Forex.
Here are the 10 important facts about the block deal:
1) Citigroup Inc. sold its 9.85% stake in HDFC. A total of 145.3 million shares were sold.
2) The average price for one share was Rs 657.56.
3) Citi will get $1.9 billion from the transaction at the current exchange rate, resulting in a pre-tax gain of $1.1 billion (Rs 5,490 crore), and an after-tax gain of approximately $722 million (Rs 3,550 crore).
4) Citi had earlier sold 1.6% stake in HDFC in June 2011.
5) Citi sold its stake because it needed additional capital under Basel 3 norms. Basel 3 is a global regulatory standard on bank capital adequacy, stress testing and market liquidity risk. It was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the late-2000s financial crisis.
6) Other foreign banks like HSBC and Goldman have also been exiting assets not seen as "core". Citi's investment in HDFC was largely financial and the ability to convert HDFC investment to a strategic investment was limited.
7) The book was oversubscribed 2-2.5 times indicating the strong demand for HDFC, which is India's top mortgage lender.
8) Foreign investors like Aberdeen Asset, Capital International, Fidelity, JPMorgan, Ontario VC Fund and Temasek bought shares from Citi. Domestic investors like ICICI Prudential also bought shares.
9) "Citi selling its stake has nothing to do with the company. The capital requirement of American banks has been increased and because Citi needs to shore up their capital, they have sold their stake. The good thing is the entire stake has been sold in one go, so there is no overhang and the other good thing is the demand for such a large issue was high," Keki Mistry, Vice Chairman & MD of HDFC
10) "We are pleased with the results of our investment in HDFC and will continue to value our long-standing relationship with the company. Citi remains deeply committed to India and we continue to focus on growth opportunities for our franchise in this very important market," said Pramit Jhaveri, Chief Executive Officer of Citi India.
1) Citigroup Inc. sold its 9.85% stake in HDFC. A total of 145.3 million shares were sold.
2) The average price for one share was Rs 657.56.
3) Citi will get $1.9 billion from the transaction at the current exchange rate, resulting in a pre-tax gain of $1.1 billion (Rs 5,490 crore), and an after-tax gain of approximately $722 million (Rs 3,550 crore).
4) Citi had earlier sold 1.6% stake in HDFC in June 2011.
5) Citi sold its stake because it needed additional capital under Basel 3 norms. Basel 3 is a global regulatory standard on bank capital adequacy, stress testing and market liquidity risk. It was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the late-2000s financial crisis.
6) Other foreign banks like HSBC and Goldman have also been exiting assets not seen as "core". Citi's investment in HDFC was largely financial and the ability to convert HDFC investment to a strategic investment was limited.
7) The book was oversubscribed 2-2.5 times indicating the strong demand for HDFC, which is India's top mortgage lender.
8) Foreign investors like Aberdeen Asset, Capital International, Fidelity, JPMorgan, Ontario VC Fund and Temasek bought shares from Citi. Domestic investors like ICICI Prudential also bought shares.
9) "Citi selling its stake has nothing to do with the company. The capital requirement of American banks has been increased and because Citi needs to shore up their capital, they have sold their stake. The good thing is the entire stake has been sold in one go, so there is no overhang and the other good thing is the demand for such a large issue was high," Keki Mistry, Vice Chairman & MD of HDFC
10) "We are pleased with the results of our investment in HDFC and will continue to value our long-standing relationship with the company. Citi remains deeply committed to India and we continue to focus on growth opportunities for our franchise in this very important market," said Pramit Jhaveri, Chief Executive Officer of Citi India.
If history is any guide (and it usually is!), the recent successful completion of the Greek Bond Swap following the announcement of the third bailout package , is likely to provide only temporary relief before another debt crisis engulfs the Eurozone down the road. Scott Minerd, the CIO of Guggenheim Partners (and an ex-colleague from my Morgan Stanley days!) , draws parallels between the current debt crisis and financial crises which dominated the financial landscape in Europe during the interwar periods – with poster child of current European woes – Greece - being replaced then by Germany. To summarise:
-During the period 1918 to 1939, European nations were also saddled with huge debts without the means to repay them, and lurched from one crisis to another, with a series of bailout plans providing only temporary relief but not solving the fundamental problem.
-After the ending of WW1 in 1918, punitive war reparations were imposed on Germany amounting to 300% of its GDP. Other nations were also heavily indebted as a result of financing the War – UK (154% of GDP), France (258% of GDP) and Italy (153% of GDP).
-Then, as now, there were strict demands for austerity plans, refusals to accept losses on certain debts, missed deadlines and bailout plans which ultimately failed, only to be replaced by another bailout plan.
-Germany lacked the ability to repay its enormous debt, and spent the next 14 years on multiple restructurings, occasional payments and numerous defaults. War devastated countries like France demanded full payment on the debt, and Germany responded by printing more and more money leading to hyperinflation (with eventually 1 US$ being equal to 4 trillion marks!).
-The first restructuring of Germany's war debt occurred in 1924 with the Dawes plan –which focused on financial reforms and involved massive lending by American banks to stimulate growth to help repay the debt.
-The second restructuring took place in 1929 with the Young plan – which reduced Germany's debt by 50% and a 58 year repayment period. However, the stock market crash of 1929 and the onset of the Great Depression put a hold on all repayments.
-Another restructuring was attempted in 1932, with a proposal made to eliminate Germany's debt (to Europe) contingent on the US writing of all debt owed to it by other European nations – this was rejected by the US congress (and eerily similar to the ECB refusing to take losses on Greek debt).
-Eventually currency debasement emerged as the only viable economic strategy, as nations abandoned the gold standard in an attempt to inflate away their debt and kick start their economies. Countries which left the gold standard recovered faster from the Great Depression than countries which remained.
-Ben Bernanke, in his well known 1991 paper, concluded that "a mismanaged interwar gold standard was responsible for the worldwide deflation of the late 1920s and early 1930s". He noted that countries which held onto the gold standard the longest (i.e. the US) suffered most from the Great Depression.
-The period of the 1920s was one of very easy monetary policy and robust economic expansion, despite Europe being mired in excessive debt and deep structural problems.
-The strategy of currency debasement is prevalent today, with the aggressive monetary easing by the Fed, the ECB, the BOE and the BOJ. And this is unlikely to end anytime soon.
-Based on Assets-to-GDP ratios the ECB is now the largest quantitative easer in the world (32%) followed closely by the BOJ (which is projected to be at 33% after completion of its programme) , the BOE (24%) and finally the Fed (19%).
-However, austerity programmes are simultaneously being imposed by governments – making it akin to "pushing on the accelerator while standing down on the brake". It is just a matter of time before serial restructuring sagas resume.
-To put it into a time perspective – Germany finally repaid its war debt with a $94 million payment on October 3, 2010 – 98 years after the end of WW1!
Investment outlook:
-The US has now entered a period of self-sustaining economic expansion, driven primarily by the Fed's (and now supported by the ECB) monetary policies making the US the economic locomotive of the global economy. This is bullish for all US risk assets-equities, high-yield bonds and bank loans.
-The situation is similar to the aftermath of the LTCM crisis in 1998, when the Fed eased aggressively leading to a major bull market in equities from 1998 until 2000.
-The Fed is unlikely to change its stance on monetary easing given the three risks facing the global economy – continuation of the European debt problem, a slowdown in emerging markets and a potential hard landing in China. Despite strong job growth numbers in recent months, Bernanke told the Senate Committee on February 7 that the job market is a "long way" from returning to normal, signalling that Fed policy will remain aggressive.
-With the Fed pleading to keep rates low until 2014, the Taylor rule suggests that rates will remain too low for too long. The improving US economy should upward pressure on interest rates over the next 6 to 12 months. Treasuries are exceptionally overvalued and are likely to yield a total negative return in 2012 – something which has only happened 3 times (1994, 1999, 2009) over the last 38 years .
-There are consequences to these actions as we set the stage for another crash in a few years – but risk assets should produce healthy returns in the interim.
-Europe is on the brink of falling into a recession following a negative GDP number for the fourth quarter of 2011 – a significant debasement of the Euro is on the horizon and the slowdown will put pressure on emerging markets and China as their export markets suffer.
A fascinating perspective – and the parallels between Germany in the 1920s and Greece today are rather illuminating. One would have thought that Germany would have learnt its lessons and therefore handled the current crisis differently – but that would have taken tremendous political will which is sorely lacking today! I agree with his view that risk assets are likely to perform well over the next few years – but do not expect a significant uptrend in interest rates until 2014 as further QE policies are likely to keep a lid on rates (and any significant sell-off should be viewed as a temporary buying opportunity) . In addition, while emerging markets growth is likely to slow down, EM equity markets are likely to perform well as the tightening monetary policies undertaken over the last year are reversed.
The significant factor over the next few years is the competitive currency debasement in the developed world, as each country aggressively pursues that objective de facto via further QE programmes. There are different ways to look at the relative scale of QE policies – assets-to-GDP ratios as described above is one method – another is looking at the increase in the monetary base from pre-crisis levels (as espoused by Nomura's Richard Koo) – on this basis the Fed is the most aggressive having increased its monetary base by 3.21 times, the BOE by 2.97, the BOJ by 3.13 (but over a longer period) and the ECB by a relatively smaller 1.96. So it seems that the ECB still has a lot of catching-up to do (about 1 trillion Euro!).
A yet another way to look at this is to take a simple ratio of the central bank assets – and the ratio between the assets of the Fed and the ECB have tracked the Eur/Usd exchange rate closely over the last few years as the graph below illustrates (via Zero Hedge). Recently, a large gap has opened up between the two implying either a rather large fall in the Euro (and a sharp fall in risk assets) or QE3 ($650-700BN) by the Fed. I suspect it is the latter or even perhaps the first quickly followed by the latter (as what happened in 2010 and 2011).
To follow-up on last week's newsletter on the unprecedented size of balance sheet expansions (i.e. QE) undertaken by the 8 major central banks, I now focus on looking at the impact of QE on asset markets and the economy. There is considerable debate on this issue, much of it clouded by ideological biases and pre-(mis)conceptions (as seems to be the norm nowadays in an increasingly polarised world!), so it is helpful to consider research which relies on data analysis to draw conclusions (i.e. a deductive rather than an inductive approach). With that aim in mind, I summarise below an insightful note by the economist and financial advisor Gavyn Davies in his FT blog (http://blogs.ft.com/gavyndavies/2012/01/25/asset-market-returns-in-a-liquidity-trap/#axzz1lbDioV8Z ):
-The weight of empirical evidence since QE started in 2008 supports the current view that QE has a positive impact on reducing long term bond yields, increasing real GDP growth and asset prices.
-Estimates on the reduction in long-term bond yields vary, with the BIS on one end estimating the impact to be a reduction of 0.25%, while the BOE and several studies in the US conclude that the reduction is 1.0% or more. The graphs below illustrate this relationship clearly and demonstrate that yield curves have flattened substantially since QE began, supporting the latter view.
-This empirical evidence refutes the traditional view that under a zero interest rate environment, investors should be indifferent to holding cash or bonds – with bond prices moving substantially higher it is clear that investors have a strong preference for holding longer term bonds which provide some return.
-However, there is a lower limit to bond yields, as suggested by the Keynesian liquidity trap. Japanese experience suggest this to be 1.3%, in which case US treasury bonds with maturities up to 5 years have already reached their lower limit- leaving the longer maturities for the Fed to focus its efforts on. In addition, the Fed could purchase mortgages and private securities to push down their spreads.
-In a QE environment, with the central bank balance sheets taking on more risk, the private sector attempts to restore its asset portfolio risk levels to those prevailing prior to the start of the crisis by purchasing riskier assets like equities. The BOE study suggests that equity prices have moved up by 20% in response to QE in the UK.
-Various studies (by the Bank of Italy and others) also suggests that QE has had a positive impact on the real economy – boosting GDP growth by 1.5% in the UK and 0.6-3.0% in the US. In addition, inflation rose (as desired by central banks) by 1.0%.
-However, the evidence also seems to indicate that the initial bout of QE had the maximum impact on bond yields, and subsequent doses produced smaller declines. This is likely to continue being the case going forward. In addition, the long-term positive correlation between central bank balance sheets and inflation is worrisome.
-In conclusion, central bankers are in general agreement that their experiment with QE has worked so far, providing a far better result than what might have been the alternative.
An interesting note, which provides ample evidence that QE does work. Martin Feldstein (not quite a supporter of Keynesian policies I might add!) had also written a note which analysed clearly the specific positive impact of QE on the fourth quarter GDP growth in 2010 (http://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/feldstein33/English ). Yes, there are likely to be unintended consequences (higher commodity prices, currency wars to name a few) but it is clearly the lesser of the evils once the alternative scenario ( a depression) is considered. As the noted economist Irving Fisher noted in his classic study of "Debt-Deflation Theory of Depressions " in 1933 (an analysis of various depressions over the previous century ) to make a point on why a reflationary policy should be pursued in the face of a severe economic downturn: "it is silly and immoral to let nature take her course as it is for a physician to ignore a case of pneumonia". To extend that thought further – a new drug to treat a patient suffering from a serious illness, is preferable (despite its potential side-effects) than letting nature takes its course and risking far more serious consequences!
So what size of further QEs can we expect from the Fed over the next few years? – I came across an interesting chart (from Casey Research) which totals the QE to date which has been required to keep short-term rates at zero, and extrapolates that number to estimate that $2 trillion of further QE could be required to keep them at zero until 2014 (which is the current stated goal of the Fed).
A very early Stock market indicator? (from Tom McClellan market report via Pragmatic Capitalist):
An intriguing chart below which looks at the Commitment of Traders (COT) data on eurodollar (interest rate deposit) futures to predict stock market movements a year in advance. Sceptical?! Read the following quotes from two reports – Feb 8, 2012 and May, 2011:
Feb 8, 2012:
-"For almost a year, we have known that a top was due to arrive in February 2012".
- "The next 3 months show a sideways to downward structure in the eurodollar COT data, and the implication is that the steep price advance that we have been seeing should transition to a more sideways market".
-" The next major inflection point is due in early June, when this leading indication says that a big multi-month rally is due to begin. By then, all of the bullishness that investors are expressing now in the various sentiment indications should have turned to frustration and pessimism, creating the right setup for a big new uptrend. The hard task will be to remain patient until then, waiting for conditions to be right again".
May 27, 2011:
-"The reason I picked this chart to show this week is that it is shouting to us now that something big is coming up for the stock market between June and October. In June 2010, the commercial eurodollar futures traders had gotten all the way up to a neutral position overall. Then between June and October 2010, they moved back to a big net short position."
-"The good news for the bullish case is that once that October low is put in, this eurodollar leading indication says we should see a really strong rally into the end of the year."
-"Commercial eurodollar traders seem to "know" a year in advance what the stock market is going to do. It is not a perfect correlation, but it is a darned good one. I'm not sure what makes this work, but I have seen that it has worked great since about 1997. It may help to understand that the commercial traders of eurodollar futures are typically the big banks, who are using these futures contracts to manage their assets and fund flows. So what we are seeing in their futures trading are responses to immediate banking liquidity conditions, and those actions give us a glimpse of future liquidity conditions for the stock market. These liquidity conditions are revealed first in the banking system, and then the liquidity waves travel through the stock market a year later."
-The weight of empirical evidence since QE started in 2008 supports the current view that QE has a positive impact on reducing long term bond yields, increasing real GDP growth and asset prices.
-Estimates on the reduction in long-term bond yields vary, with the BIS on one end estimating the impact to be a reduction of 0.25%, while the BOE and several studies in the US conclude that the reduction is 1.0% or more. The graphs below illustrate this relationship clearly and demonstrate that yield curves have flattened substantially since QE began, supporting the latter view.
-This empirical evidence refutes the traditional view that under a zero interest rate environment, investors should be indifferent to holding cash or bonds – with bond prices moving substantially higher it is clear that investors have a strong preference for holding longer term bonds which provide some return.
-However, there is a lower limit to bond yields, as suggested by the Keynesian liquidity trap. Japanese experience suggest this to be 1.3%, in which case US treasury bonds with maturities up to 5 years have already reached their lower limit- leaving the longer maturities for the Fed to focus its efforts on. In addition, the Fed could purchase mortgages and private securities to push down their spreads.
-In a QE environment, with the central bank balance sheets taking on more risk, the private sector attempts to restore its asset portfolio risk levels to those prevailing prior to the start of the crisis by purchasing riskier assets like equities. The BOE study suggests that equity prices have moved up by 20% in response to QE in the UK.
-Various studies (by the Bank of Italy and others) also suggests that QE has had a positive impact on the real economy – boosting GDP growth by 1.5% in the UK and 0.6-3.0% in the US. In addition, inflation rose (as desired by central banks) by 1.0%.
-However, the evidence also seems to indicate that the initial bout of QE had the maximum impact on bond yields, and subsequent doses produced smaller declines. This is likely to continue being the case going forward. In addition, the long-term positive correlation between central bank balance sheets and inflation is worrisome.
-In conclusion, central bankers are in general agreement that their experiment with QE has worked so far, providing a far better result than what might have been the alternative.
An interesting note, which provides ample evidence that QE does work. Martin Feldstein (not quite a supporter of Keynesian policies I might add!) had also written a note which analysed clearly the specific positive impact of QE on the fourth quarter GDP growth in 2010 (http://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/feldstein33/English ). Yes, there are likely to be unintended consequences (higher commodity prices, currency wars to name a few) but it is clearly the lesser of the evils once the alternative scenario ( a depression) is considered. As the noted economist Irving Fisher noted in his classic study of "Debt-Deflation Theory of Depressions " in 1933 (an analysis of various depressions over the previous century ) to make a point on why a reflationary policy should be pursued in the face of a severe economic downturn: "it is silly and immoral to let nature take her course as it is for a physician to ignore a case of pneumonia". To extend that thought further – a new drug to treat a patient suffering from a serious illness, is preferable (despite its potential side-effects) than letting nature takes its course and risking far more serious consequences!
So what size of further QEs can we expect from the Fed over the next few years? – I came across an interesting chart (from Casey Research) which totals the QE to date which has been required to keep short-term rates at zero, and extrapolates that number to estimate that $2 trillion of further QE could be required to keep them at zero until 2014 (which is the current stated goal of the Fed).
A very early Stock market indicator? (from Tom McClellan market report via Pragmatic Capitalist):
An intriguing chart below which looks at the Commitment of Traders (COT) data on eurodollar (interest rate deposit) futures to predict stock market movements a year in advance. Sceptical?! Read the following quotes from two reports – Feb 8, 2012 and May, 2011:
Feb 8, 2012:
-"For almost a year, we have known that a top was due to arrive in February 2012".
- "The next 3 months show a sideways to downward structure in the eurodollar COT data, and the implication is that the steep price advance that we have been seeing should transition to a more sideways market".
-" The next major inflection point is due in early June, when this leading indication says that a big multi-month rally is due to begin. By then, all of the bullishness that investors are expressing now in the various sentiment indications should have turned to frustration and pessimism, creating the right setup for a big new uptrend. The hard task will be to remain patient until then, waiting for conditions to be right again".
May 27, 2011:
-"The reason I picked this chart to show this week is that it is shouting to us now that something big is coming up for the stock market between June and October. In June 2010, the commercial eurodollar futures traders had gotten all the way up to a neutral position overall. Then between June and October 2010, they moved back to a big net short position."
-"The good news for the bullish case is that once that October low is put in, this eurodollar leading indication says we should see a really strong rally into the end of the year."
-"Commercial eurodollar traders seem to "know" a year in advance what the stock market is going to do. It is not a perfect correlation, but it is a darned good one. I'm not sure what makes this work, but I have seen that it has worked great since about 1997. It may help to understand that the commercial traders of eurodollar futures are typically the big banks, who are using these futures contracts to manage their assets and fund flows. So what we are seeing in their futures trading are responses to immediate banking liquidity conditions, and those actions give us a glimpse of future liquidity conditions for the stock market. These liquidity conditions are revealed first in the banking system, and then the liquidity waves travel through the stock market a year later."




